Journal Description
Mathematics
Mathematics
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal which provides an advanced forum for studies related to mathematics, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The European Society for Fuzzy Logic and Technology (EUSFLAT) and International Society for the Study of Information (IS4SI) are affiliated with Mathematics and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Mathematics) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Mathematics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 13 topical sections.
- Companion journals for Mathematics include: Foundations, AppliedMath, Analytics, International Journal of Topology, Geometry and Logics.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.3 (2022)
Latest Articles
Community-Aware Evolution Similarity for Link Prediction in Dynamic Social Networks
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 285; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020285 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The link prediction problem is a time-evolving model in network science that has simultaneously abetted myriad applications and experienced extensive methodological improvement. Inferring the possibility of emerging links in dynamic social networks, also known as the dynamic link prediction task, is complex and
[...] Read more.
The link prediction problem is a time-evolving model in network science that has simultaneously abetted myriad applications and experienced extensive methodological improvement. Inferring the possibility of emerging links in dynamic social networks, also known as the dynamic link prediction task, is complex and challenging. In contrast to the link prediction in cross-sectional networks, dynamic link prediction methods need to cater to the actor-level temporal changes and associated evolutionary information regarding their micro- (i.e., link formation/deletion) and mesoscale (i.e., community formation) network structure. With the advent of abundant community detection algorithms, the research community has examined community-aware link prediction strategies in static networks. However, the same task in dynamic networks where, apart from the actors and links among them, their community pattern is also dynamic, is yet to be explored. Evolutionary community-aware information, including the associated link structure and temporal neighborhood changes, can effectively be mined to build dynamic similarity metrics for dynamic link prediction. This study aims to develop and integrate such dynamic features with machine learning algorithms for link prediction tasks in dynamic social networks. It also compares the performances of these features against well-known similarity metrics (i.e., ResourceAllocation) for static networks and a time series-based link prediction strategy in dynamic networks. These proposed features achieved high-performance scores, representing them as prospective candidates for both dynamic link prediction tasks and modeling the network growth.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applied Network Analysis and Data Science)
Open AccessArticle
Trends and Extremes in Time Series Based on Fuzzy Logic
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 284; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020284 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The authors develop the theory of discrete differentiation and, on its basis, solve the problem of detecting trends in records, using the idea of the connection between trends and derivatives in classical analysis but implementing it using fuzzy logic methods. The solution to
[...] Read more.
The authors develop the theory of discrete differentiation and, on its basis, solve the problem of detecting trends in records, using the idea of the connection between trends and derivatives in classical analysis but implementing it using fuzzy logic methods. The solution to this problem is carried out by constructing fuzzy measures of the trend and extremum for a recording. The theoretical justification of the regression approach to classical differentiation in the continuous case given in this work provides an answer to the question of what discrete differentiation is, which is used in constructing fuzzy measures of the trend and extremum. The detection of trends using trend and extremum measures is more stable and of higher quality than using traditional data analysis methods, which consist in studying the intervals of constant sign of the derivative for a piecewise smooth approximation of the original record. The approach proposed by the authors, due to its implementation within the framework of fuzzy logic, is largely focused on the researcher analyzing the record and at the same time uses the idea of multiscale. The latter circumstance provides a more complete and in-depth understanding of the process behind the recording.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fuzzy Logic and Computational Intelligence)
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Approach to Enhance DIRECT-Type Algorithms for Hyper-Rectangle Identification
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 283; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020283 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
This paper introduces novel enhancements to the most recent versions of DIRECT-type algorithms, especially when dealing with solutions located at the hyper-rectangle vertices. The BIRECT algorithm encounters difficulties in efficiently sampling points at the boundaries of the feasible region, leading to potential slowdowns
[...] Read more.
This paper introduces novel enhancements to the most recent versions of DIRECT-type algorithms, especially when dealing with solutions located at the hyper-rectangle vertices. The BIRECT algorithm encounters difficulties in efficiently sampling points at the boundaries of the feasible region, leading to potential slowdowns in convergence. This issue is particularly pronounced when the optimal solution resides near the boundary. Our research explores diverse approaches, with a primary focus on incorporating a grouping strategy for hyper-rectangles of similar sizes. This categorization into different classes, constrained by a predefined threshold, aims to enhance computational efficiency, particularly involving a substantial number of hyper-rectangles of varying sizes. To further improve the new algorithm’s efficiency, we implemented a mechanism to prevent oversampling and mitigate redundancy in sampling at shared vertices within descendant sub-regions. Comparisons with several DIRECT-type algorithms highlight the promising nature of the proposed algorithms as a global optimization solution. Statistical analyses, including Friedman and Wilcoxon tests, demonstrated the effectiveness of the improvements introduced in this new algorithm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Engineering Mathematics)
Open AccessArticle
Finite Element Method of Functionally Graded Shape Memory Alloy Based on UMAT
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 282; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020282 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Functionally graded shape memory alloy (FG-SMA) is widely used in practical engineering regions due to it possessing the excellent properties of both FG material and SMA material. In this paper, the incremental constitutive equation of SMA was established by using the concept of
[...] Read more.
Functionally graded shape memory alloy (FG-SMA) is widely used in practical engineering regions due to it possessing the excellent properties of both FG material and SMA material. In this paper, the incremental constitutive equation of SMA was established by using the concept of a shape memory factor. On this basis, the secondary development function of the ABAQUS software 2023 was used to write the user-defined material subroutine (UMAT). The phase transformation and mechanical behavior of transverse and axial FG NiTi SMA cantilever beams under concentrated load at free ends were numerically simulated by discrete modeling. Numerical results show that the stress and shape memory factor were distributed asymmetrically along the thickness direction of the transverse FG-SMA cantilever beam, while the stress and the shape memory factor distributed symmetrically along the thickness direction of the cross section of the axial FG-SMA cantilever beam. The bearing capacity of the axial FG-SMA cantilever beam is stronger than the SMA homogeneous cantilever beam, but weaker than the transverse FG-SMA cantilever beam. The load-bearing capacity of the transverse FG-SMA cantilever beam is twice that of the axial FG-SMA cantilever beam under the same functionally graded parameters and deflection conditions. The discrete modeling method of FG-SMA beams proposed in this paper can simulate the phase transformation and mechanical behavior of an FG-SMA beam well, which provides a reference for the practical application and numerical calculation of FG-SMA structures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Engineering Mathematics)
►▼
Show Figures
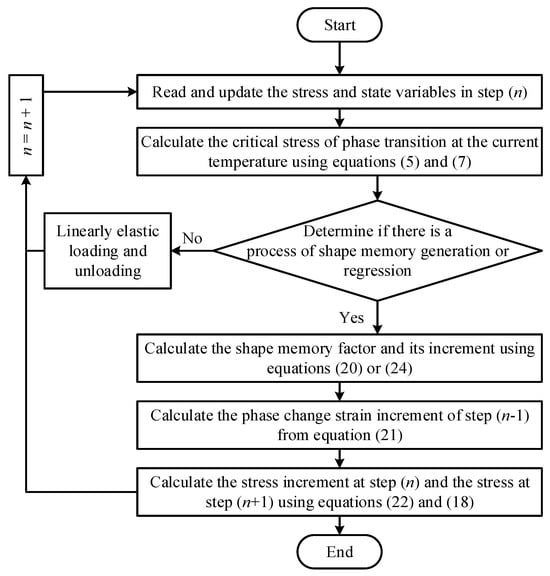
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Evolutionary Algorithm for Task Clustering and Scheduling in IoT Edge Computing
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 281; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020281 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) edge is an emerging technology of sensors and devices that communicate real-time data to a network. IoT edge computing was introduced to handle the latency concerns related to cloud computing data management, as the data are processed closer
[...] Read more.
The Internet of Things (IoT) edge is an emerging technology of sensors and devices that communicate real-time data to a network. IoT edge computing was introduced to handle the latency concerns related to cloud computing data management, as the data are processed closer to their point of origin. Clustering and scheduling tasks on IoT edge computing are considered a challenging problem due to the diverse nature of task and resource characteristics. Metaheuristics and optimization methods are widely used in IoT edge task clustering and scheduling. This paper introduced a new task clustering and scheduling mechanism using differential evolution optimization on IoT edge computing. The proposed mechanism aims to optimize task clustering and scheduling to find optimal execution times for submitted tasks. The proposed mechanism for task clustering is based on the degree of similarity of task characteristics. The proposed mechanisms use an evolutionary mechanism to distribute system tasks across suitable IoT edge resources. The clustering tasks process categorizes tasks with similar requirements and then maps them to appropriate resources. To evaluate the proposed differential evolution mechanism for IoT edge task clustering and scheduling, this study conducted several simulation experiments against two established mechanisms: the Firefly Algorithm (FA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). The simulation configuration was carefully created to mimic real-world IoT edge computing settings to ensure the proposed mechanism’s applicability and the simulation results’ relevance. In the heavyweight workload scenario, the proposed DE mechanism started with an execution time of 916.61 milliseconds, compared to FA’s 1092 milliseconds and PSO’s 1026.09 milliseconds. By the 50th iteration, the proposed DE mechanism had reduced its execution time significantly to around 821.27 milliseconds, whereas FA and PSO showed lesser improvements, with FA at approximately 1053.06 milliseconds and PSO stabilizing at 956.12 milliseconds. The simulation results revealed that the proposed differential evolution mechanism for edge task clustering and scheduling outperforms FA and PSO regarding system efficiency and stability, significantly reducing execution time and having minimal variation across simulation iterations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Combinatorial Optimization: Trends and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
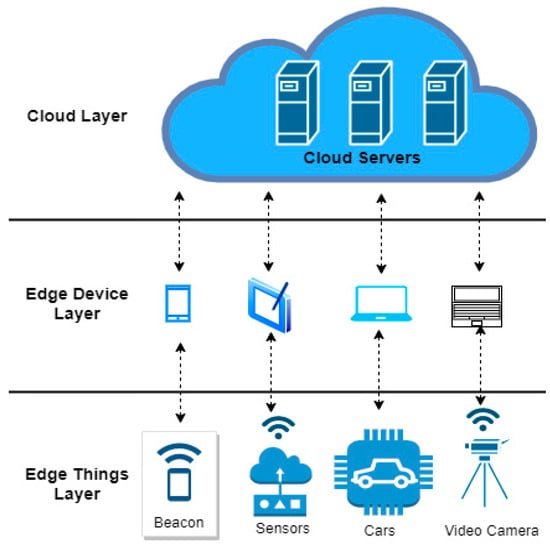
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Neural Network Algorithm with Reinforcement Learning for Microgrid Techno-Economic Optimization
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 280; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020280 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Hybrid energy systems (HESs) are gaining prominence as a practical solution for powering remote and rural areas, overcoming limitations of conventional energy generation methods, and offering a blend of technical and economic benefits. This study focuses on optimizing the sizes of an autonomous
[...] Read more.
Hybrid energy systems (HESs) are gaining prominence as a practical solution for powering remote and rural areas, overcoming limitations of conventional energy generation methods, and offering a blend of technical and economic benefits. This study focuses on optimizing the sizes of an autonomous microgrid/HES in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, incorporating solar photovoltaic energy, wind turbine generators, batteries, and a diesel generator. The innovative reinforcement learning neural network algorithm (RLNNA) is applied to minimize the annualized system cost (ASC) and enhance system reliability, utilizing hourly wind speed, solar irradiance, and load behavior data throughout the year. This study validates RLNNA against five other metaheuristic/soft-computing approaches, demonstrating RLNNA’s superior performance in achieving the lowest ASC at USD 1,219,744. This outperforms SDO and PSO, which yield an ASC of USD 1,222,098.2, and MRFO, resulting in an ASC of USD 1,222,098.4, while maintaining a loss of power supply probability (LPSP) of 0%. RLNNA exhibits faster convergence to the global solution than other algorithms, including PSO, MRFO, and SDO, while MRFO, PSO, and SDO show the ability to converge to the optimal global solution. This study concludes by emphasizing RLNNA’s effectiveness in optimizing HES sizing, contributing valuable insights for off-grid energy systems in remote regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Modeling, Optimization and Algorithms for Power Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
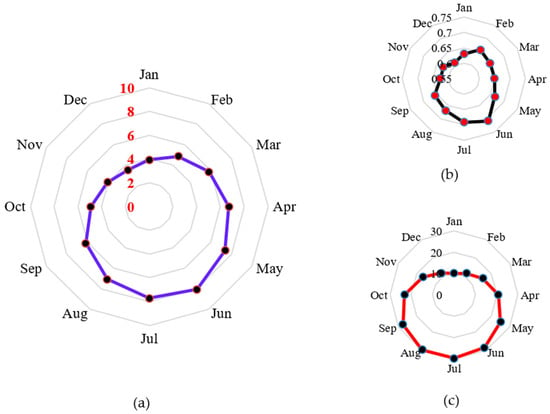
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Convergence and Boundedness of Solutions to SFDEs with the G-Framework
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 279; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020279 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Generally, stochastic functional differential equations (SFDEs) pose a challenge as they often lack explicit exact solutions. Consequently, it becomes necessary to seek certain favorable conditions under which numerical solutions can converge towards the exact solutions. This article aims to delve into the convergence
[...] Read more.
Generally, stochastic functional differential equations (SFDEs) pose a challenge as they often lack explicit exact solutions. Consequently, it becomes necessary to seek certain favorable conditions under which numerical solutions can converge towards the exact solutions. This article aims to delve into the convergence analysis of solutions for stochastic functional differential equations by employing the framework of G-Brownian motion. To establish the goal, we find a set of useful monotone type conditions and work within the space
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Functional Differential Equations and Epidemiological Modelling, 2nd Edition)
Open AccessArticle
A
by
and
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 278; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020278 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
In this paper, we employed the
In this paper, we employed the
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics: Methods and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
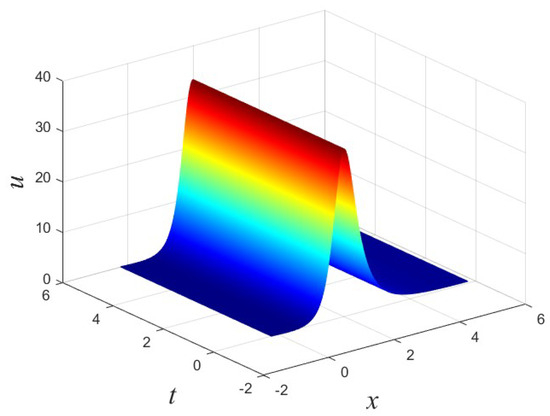
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Approximate Analytical Solutions for Strongly Coupled Systems of Singularly Perturbed Convection–Diffusion Problems
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 277; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020277 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work presents a reliable algorithm to obtain approximate analytical solutions for a strongly coupled system of singularly perturbed convection–diffusion problems, which exhibit a boundary layer at one end. The proposed method involves constructing a zero-order asymptotic approximate solution for the original system.
[...] Read more.
This work presents a reliable algorithm to obtain approximate analytical solutions for a strongly coupled system of singularly perturbed convection–diffusion problems, which exhibit a boundary layer at one end. The proposed method involves constructing a zero-order asymptotic approximate solution for the original system. This approximation results in the formation of two systems: a boundary layer system with a known analytical solution and a reduced terminal value system, which is solved analytically using an improved residual power series approach. This approach combines the residual power series method with Padé approximation and Laplace transformation, resulting in an approximate analytical solution with higher accuracy compared to the conventional residual power series method. In addition, error estimates are extracted, and illustrative examples are provided to demonstrate the accuracy and effectiveness of the method.
Full article
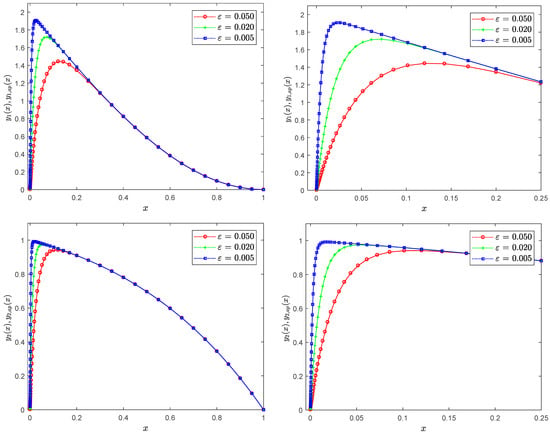
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mathematical Models for the Design of GRID Systems to Solve Resource-Intensive Problems
by
, , , , , , and
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 276; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020276 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Artificial neural networks are successfully used to solve a wide variety of scientific and technical problems. The purpose of the study is to increase the efficiency of distributed solutions for problems involving structural-parametric synthesis of neural network models of complex systems based on
[...] Read more.
Artificial neural networks are successfully used to solve a wide variety of scientific and technical problems. The purpose of the study is to increase the efficiency of distributed solutions for problems involving structural-parametric synthesis of neural network models of complex systems based on GRID (geographically disperse computing resources) technology through the integrated application of the apparatus of evolutionary optimization and queuing theory. During the course of the research, the following was obtained: (i) New mathematical models for assessing the performance and reliability of GRID systems; (ii) A new multi-criteria optimization model for designing GRID systems to solve high-resource computing problems; and (iii) A new decision support system for the design of GRID systems using a multi-criteria genetic algorithm. Fonseca and Fleming’s genetic algorithm with a dynamic penalty function was used as a method for solving the stated multi-constrained optimization problem. The developed program system was used to solve the problem of choosing an effective structure of a centralized GRID system that was configured to solve the problem of structural-parametric synthesis of neural network models. To test the proposed approach, a Pareto-optimal configuration of the GRID system was built with the following characteristics: average performance–103.483 GFLOPS, cost–500 rubles per day, availability rate–99.92%, and minimum performance–51 GFLOPS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Analysis and Application of Mathematical Optimization Algorithms)
►▼
Show Figures
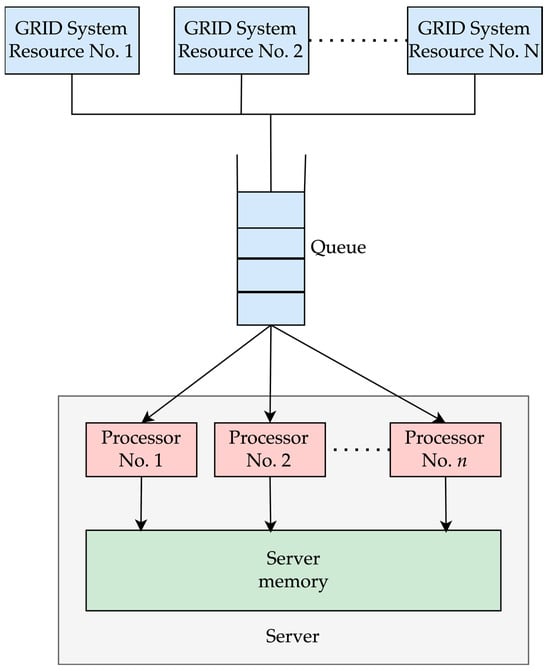
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predator–Prey Dynamics and Ideal Free Distribution in a Heterogeneous Environment
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 275; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020275 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The concept of an ideal free distribution (IFD) is extended to a predator–prey system in a heterogeneous environment. We consider reaction–diffusion–advection equations which describe the evolution of spatial distributions of predators and prey under directed migration. Modification of local interaction terms is introduced,
[...] Read more.
The concept of an ideal free distribution (IFD) is extended to a predator–prey system in a heterogeneous environment. We consider reaction–diffusion–advection equations which describe the evolution of spatial distributions of predators and prey under directed migration. Modification of local interaction terms is introduced, if some coefficients depend on resource. Depending on coefficients of local interaction, the different scenarios of predator distribution are possible. We pick out three cases: proportionality to prey (and respectively to resource), indifferent distribution and inversely proportional to the prey. These scenarios apply in the case of nonzero diffusion and taxis under additional conditions on diffusion and migration rates. We examine migration functions for which there are explicit stationary solutions with nonzero densities of both species. To analyze solutions with violation of the IFD conditions, we apply asymptotic expansions and a numerical approach with staggered grids. The results for a two-dimensional domain with no-flux boundary conditions are presented.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Theoretical and Mathematical Ecology)
►▼
Show Figures
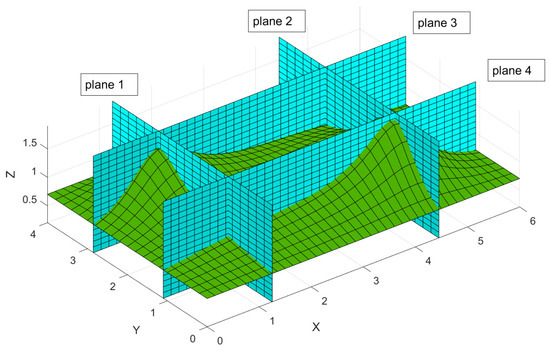
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
How Chinese Undergraduate Students’ Perceptions of Assessment for Learning Influence Their Responsibility for First-Year Mathematics Courses
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 274; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020274 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Assessment for learning (AFL) has been associated with curriculum and teaching reform for the past three decades. However, studies on undergraduate students’ perceptions of their mathematics teachers’ AFL practices are still very limited in the Chinese higher education context. This quantitative study investigated
[...] Read more.
Assessment for learning (AFL) has been associated with curriculum and teaching reform for the past three decades. However, studies on undergraduate students’ perceptions of their mathematics teachers’ AFL practices are still very limited in the Chinese higher education context. This quantitative study investigated three independent variables—teacher formal feedback and support, interactive dialog and peer collaboration, and learning-oriented assessment—that influence undergraduate students’ ability to take responsibility for their learning through the mediation of the factor of active engagement with subject matter in first-year mathematics courses. One hundred and sixty-eight students from a Chinese “double-first-class” university were recruited to provide valid questionnaire data using the convenience sampling method. Partial least-squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) was used to analyze the data. The results showed that interactive dialog and peer collaboration, as well as learning-oriented assessment, have a direct effect on students’ active engagement with the subject matter and an indirect effect on undergraduate students taking responsibility for their learning in first-year mathematics courses. In addition, learning-oriented assessment was the biggest factor influencing undergraduate students’ ability to take responsibility for their learning in first-year mathematics courses. This study contributes by developing a conceptual model and providing new insights into Chinese higher education sectors on factors that can improve undergraduate students’ ability to take responsibility for their learning.
Full article
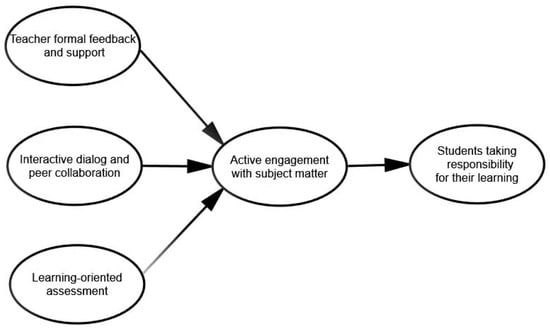
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
The Equilibrium Solutions for a Nonlinear Separable Population Model
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 273; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020273 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
The paper investigates a nonlinear model that describes population dynamics with an age structure. The fertility rate, which varies with age, follows a nonconstant pattern. The model exhibits a multiplicative structure for both fertility and mortality rates. Remarkably, this multiplicative structure renders the
[...] Read more.
The paper investigates a nonlinear model that describes population dynamics with an age structure. The fertility rate, which varies with age, follows a nonconstant pattern. The model exhibits a multiplicative structure for both fertility and mortality rates. Remarkably, this multiplicative structure renders the model separable. In this setting, it is shown that the number of births in unit time can be expressed using a system of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. The asymptotic behavior of solutions to this system has been established for a specific case. This result is significant because it provides a mathematical framework for understanding the dynamics of birth rates in certain settings. Furthermore, this paper explicitly identifies the steady-state solution and the equilibrium solution. As in any research paper, new directions of study remain open.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Predicting Critical Path of Labor Dispute Resolution in Legal Domain by Machine Learning Models Based on SHapley Additive exPlanations and Soft Voting Strategy
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 272; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020272 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
The labor dispute is one of the most common civil disputes. It can be resolved in the order of the following steps, which include mediation in arbitration, arbitration award, first-instance mediation, first-instance judgment, and second-instance judgment. The process can cease at any step
[...] Read more.
The labor dispute is one of the most common civil disputes. It can be resolved in the order of the following steps, which include mediation in arbitration, arbitration award, first-instance mediation, first-instance judgment, and second-instance judgment. The process can cease at any step when it is successfully resolved. In recent years, due to the increasing rights awareness of employees, the number of labor disputes has been rising annually. However, resolving labor disputes is time-consuming and labor-intensive, which brings a heavy burden to employees and dispute resolution institutions. Using artificial intelligence algorithms to identify and predict the critical path of labor dispute resolution is helpful for saving resources and improving the efficiency of, and reducing the cost of dispute resolution. In this study, a machine learning approach based on Shapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) and a soft voting strategy is applied to predict the critical path of labor dispute resolution. We name our approach LDMLSV (stands for Labor Dispute Machine Learning based on SHapley additive exPlanations and Voting). This approach employs three machine learning models (Random Forest, Extra Trees, and CatBoost) and then integrates them using a soft voting strategy. Additionally, SHAP is used to explain the model and analyze the feature contribution. Based on the ranking of feature importance obtained from SHAP and an incremental feature selection method, we obtained an optimal feature subset comprising 33 features. The LDMLSV achieves an accuracy of 0.90 on this optimal feature subset. Therefore, the proposed approach is a highly effective method for predicting the critical path of labor dispute resolution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computational Intelligence: Theory and Applications, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
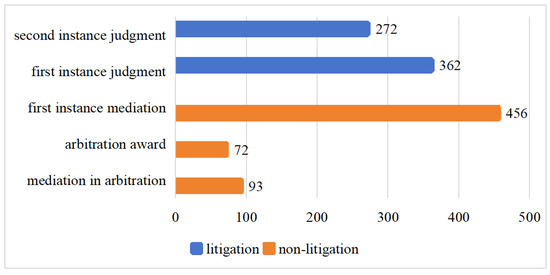
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Simulation of Heuristics for Automated Guided Vehicle Task Sequencing with Resource Sharing and Dynamic Queues
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 271; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020271 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) stand out as a paradigmatic application of Industry 4.0, requiring the seamless integration of new concepts and technologies to enhance productivity while reducing labor costs, energy consumption, and emissions. In this context, specific industrial use cases can present a
[...] Read more.
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) stand out as a paradigmatic application of Industry 4.0, requiring the seamless integration of new concepts and technologies to enhance productivity while reducing labor costs, energy consumption, and emissions. In this context, specific industrial use cases can present a significant technological and scientific challenge. This study was inspired by a real industrial application for which the existing AGV literature did not contain an already well-studied solution. The problem is related to the sequencing of assigned tasks, where the queue formation dynamics and the resource sharing define the scheduling. The combinatorial nature of the problem requires the use of advanced mathematical tools such as heuristics, simulations, or a combination of both. A heuristic procedure was developed that generates candidate task sequences, which are, in turn, evaluated in a discrete-event simulation model developed in Simul8. This combined approach allows high-quality solutions to be generated and realistically evaluated, even graphically, by stakeholders and decision makers. A number of computational experiments were developed to validate the proposed method, which opens up some future lines of research, especially when considering stochastic settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Methods and Operation Research in Logistics, Project Planning, and Scheduling, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
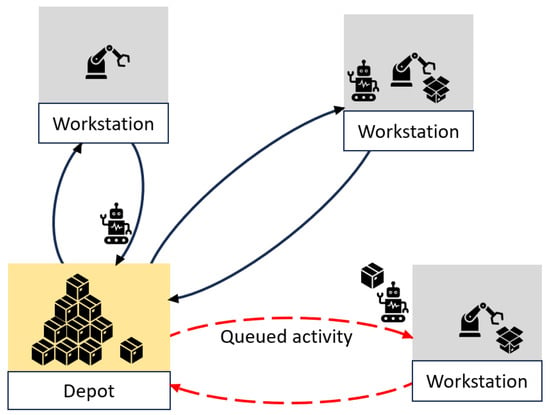
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
RNDLP: A Distributed Framework for Supporting Continuous k-Similarity Trajectories Search over Road Network
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 270; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020270 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
Continuous k-similarity trajectories search over a data stream is an important problem in the domain of spatio-temporal databases. Given a set of trajectories
Continuous k-similarity trajectories search over a data stream is an important problem in the domain of spatio-temporal databases. Given a set of trajectories
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Modeling for Parallel and Distributed Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
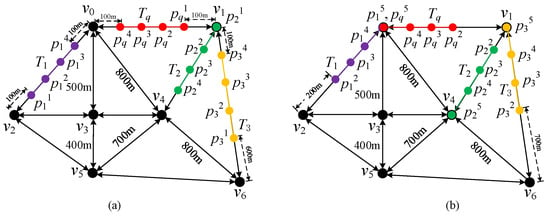
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fictitious Point Technique Based on Finite-Difference Method for 2.5D Direct-Current Resistivity Forward Problem
by
and
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 269; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020269 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
With the widespread application of the direct-current resistivity method, searching for accurate and fast-forward algorithms has become the focus of research for geophysicists and engineers. Three-dimensional forward modeling can be the best way to identify geo-electrical anomalies but are hampered by computational limitations
[...] Read more.
With the widespread application of the direct-current resistivity method, searching for accurate and fast-forward algorithms has become the focus of research for geophysicists and engineers. Three-dimensional forward modeling can be the best way to identify geo-electrical anomalies but are hampered by computational limitations because of the large amount of data. A practical compromise, or even alternative, is represented by 2.5D modeling characterized using a 3D source in a 2D medium. Thus, we develop a 2.5D direct-current resistivity forward modeling algorithm. The algorithm incorporates the finite-difference approximation and fictitious point technique that can improve the efficiency and accuracy of numerical simulation. Firstly, from the boundary value problem of the electric potential generated by the point source, the discrete expressions of the governing equation are derived from the finite-difference approach. The numerical solutions of the discrete electric potential are calculated after the approximate treatment of the boundary conditions with a finite-difference method based on a fictitious point scheme. Secondly, through the simulation of a homogeneous half-space model and a one-dimensional model, and compared with the analytical results, the correctness and stability of the finite-difference forward algorithm are verified. Lastly, through the numerical simulation for a two-dimensional model, 2.5D direct-current sounding responses are summarized, which can provide a qualitative interpretation of field data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematics in Geophysical Research)
Open AccessArticle
A Validation of the Phenomenon of Linearly Many Faults on Burnt Pancake Graphs with Its Applications
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 268; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020268 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
“Linearly many faults” is a phenomenon observed by Cheng and Lipták in which a specific structure emerges when a graph is disconnected and often occurs in various interconnection networks. This phenomenon means that if a certain number of vertices or edges are deleted
[...] Read more.
“Linearly many faults” is a phenomenon observed by Cheng and Lipták in which a specific structure emerges when a graph is disconnected and often occurs in various interconnection networks. This phenomenon means that if a certain number of vertices or edges are deleted from a graph, the remaining part either stays connected or breaks into one large component along with smaller components with just a few vertices. This phenomenon can be observed in many types of graphs and has important implications for network analysis and optimization. In this paper, we first validate the phenomenon of linearly many faults for surviving graph of a burnt pancake graph
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Graph Theory: Advanced Algorithms and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
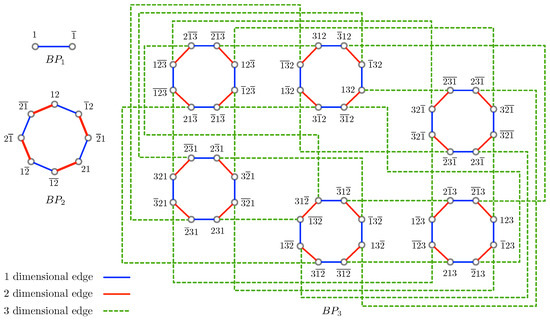
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Analysis of Blood Clot Mechanical Behavior in Relation to Blood Flow Inside the Popliteal Vein
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 267; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020267 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
In this work, blood clot behavior under the influence of the mechanical effect of blood flow was analyzed. Attention is mainly paid to the deformation of the thrombus in the event of an alternating effect of blood flow in the blood vessel of
[...] Read more.
In this work, blood clot behavior under the influence of the mechanical effect of blood flow was analyzed. Attention is mainly paid to the deformation of the thrombus in the event of an alternating effect of blood flow in the blood vessel of the human leg. It is assumed that the higher stress accumulation is associated with a decrease in the width of the lumen of the blood vessel. The idea is to represent a critical case when embolus can form. The geometry of the thrombus is selected on the basis of existing blood patterns. Modeling is performed using COMSOL Multiphysics software. The results reflect the distribution of stress and blood velocity over time. The work selected a critical case, when the formation of an embolus is possible due to the deformation of the thrombus by the blood flow. Research is important for studying the behavior of thrombus formation at different periods of time, and also taking into account the specific geometry of thrombus deformation for the purpose of predicting embolisms. The results are observed due to increased deformations in the appropriate areas of the clot, whose tests show specific blood deformation from the alternating effects of blood on different sections of the vessels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimization and Simulation in Mechanical Engineering and Computer Aided Design)
►▼
Show Figures
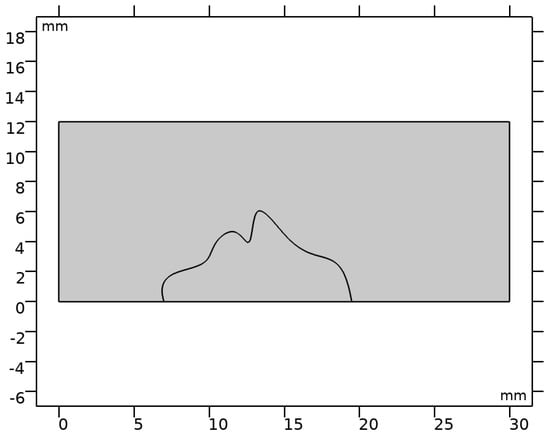
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Trajectory and Global Attractors for the Kelvin–Voigt Model Taking into Account Memory along Fluid Trajectories
Mathematics 2024, 12(2), 266; https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020266 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
This article is devoted to the study of the existence of trajectory and global attractors in the Kelvin–Voigt fluid model, taking into account memory along the trajectories of fluid motion. For the model under study, the concept of a weak solution on a
[...] Read more.
This article is devoted to the study of the existence of trajectory and global attractors in the Kelvin–Voigt fluid model, taking into account memory along the trajectories of fluid motion. For the model under study, the concept of a weak solution on a finite segment and semi-axis is introduced and the existence of their solutions is proved. The necessary exponential estimates for the solutions are established. Then, based on these estimates, the existence of trajectory and global attractors in the problem under study is proved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mathematical Problems in Fluid Mechanics)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Mathematics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Chemistry, IJMS, Mathematics, Symmetry, Computation
Molecular Topology and Computation
Topic Editors: Lorentz Jäntschi, Dusanka JanezicDeadline: 1 February 2024
Topic in
Computers, Energies, Future Internet, Information, Mathematics
Research on Blockchain Technology for Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading
Topic Editors: Pierre-Martin Tardif, Brahim El Bhiri, Bilal Abu-Salih, Kenji TanakaDeadline: 29 February 2024
Topic in
Data, Future Internet, Information, Mathematics, Symmetry
Application of Deep Learning Method in 6G Communication Technology
Topic Editors: Mohamed Abouhawwash, K. VenkatachalamDeadline: 31 March 2024
Topic in
Axioms, Computation, MCA, Mathematics, Symmetry
Mathematical Modeling
Topic Editors: Babak Shiri, Zahra AlijaniDeadline: 31 May 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Mathematics
Mathematical Modeling, Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing, with Their Applications
Guest Editor: Songting LuoDeadline: 20 January 2024
Special Issue in
Mathematics
Multiobjective Optimization: Methodology, Computational Implementation and Real Models
Guest Editors: Mariano Luque, Ana B. RuizDeadline: 31 January 2024
Special Issue in
Mathematics
Mathematics and Computation in Music
Guest Editor: Luca Andrea LudovicoDeadline: 15 February 2024
Special Issue in
Mathematics
Computational Algebraic Topology and Neural Networks in Computer Vision
Guest Editors: Rocio Gonzalez Diaz, Matthias ZeppelzauerDeadline: 29 February 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Mathematics
Multiscale Computation and Machine Learning
Collection Editors: Yalchin Efendiev, Eric Chung
Topical Collection in
Mathematics
Theoretical and Mathematical Ecology
Collection Editor: Yuri V. Tyutyunov